
Postmortem artifacts made by ants and the effect of ant activity on decompositional rates. Updated November 11,2015 Accessed: March 2, 2016.Ĭampobasso CP, Marchetti D, Introna F, Colonna MF. Kibbi A-G, Tannous Z, Kurban M, Bahhady RF, Harb DI. Subcapsular liver haematoma after cardiopulmonary resuscitation by untrained personnel. Monsuez JJ, Charniot JC, Veilhan LA, et al. Does cardiopulmonary resuscitation cause rib fractures in children? A systematic review. Forensic aspects of complications resulting from cardiopulmonary resuscitation. Rib fractures in infants due to cardiopulmonary resuscitation efforts. Frequent and rare complications of resuscitation attempts. Chest wall injuries following cardiopulmonary resuscitation. Antemortem and postmortem bruises on the skin: their differentiation. The ageing of bruises: a review and study of the colour changes with time. Post-mortem diagnosis and age estimation of infants' fractures. Klotzbach H, Delling G, Richter E, Sperhake JP, Puschel K. Histologic dating of bruises in moribund infants and young children. Chapter 14.īyard RW, Wick R, Gilbert JD, Donald T. Northfield, Ill: College of American Pathologists 2003. Spitz and Fisher's Medicolegal Investigation of Death: Guidelines for the Application of Pathology to Crime Investigation.


Forensic Pathology: Principles and Practice. Chapters 4-5.ĭolinak D, Matshes EW, Lew EO. Blunt trauma wounds and blunt trauma injuries of the trunk and extremities. For example, the cause of death of an individual who dies of pneumonia after being hospitalized for several days for treatment of blunt force injuries following a motor vehicle collision should be certified as "acute bronchopneumonia complicating blunt force injuries due to a motor vehicle accident." The manner of death should then be certified as "accident."ĭiMaio VJ, DiMaio D. It is important to understand that the designated manner of death in such scenarios must include the causal factor that made the decedent susceptible to the disease state, namely the underlying injury which initiated the chain of events ultimately leading to death. In some cases, the injury may have occurred many years before death. For example, individuals may die of infections, thromboemboli, or organ failure that occurs as a delayed result of previous blunt force trauma. Although it is important to document evidence of blunt force trauma in all autopsies, one should not immediately assume that blunt force trauma is the cause of death.įor purposes of death certification, it should be noted that blunt force trauma may be the underlying (proximate) cause of death in cases in which the immediate cause of death is a natural disease process.
#Blunt trauma skin
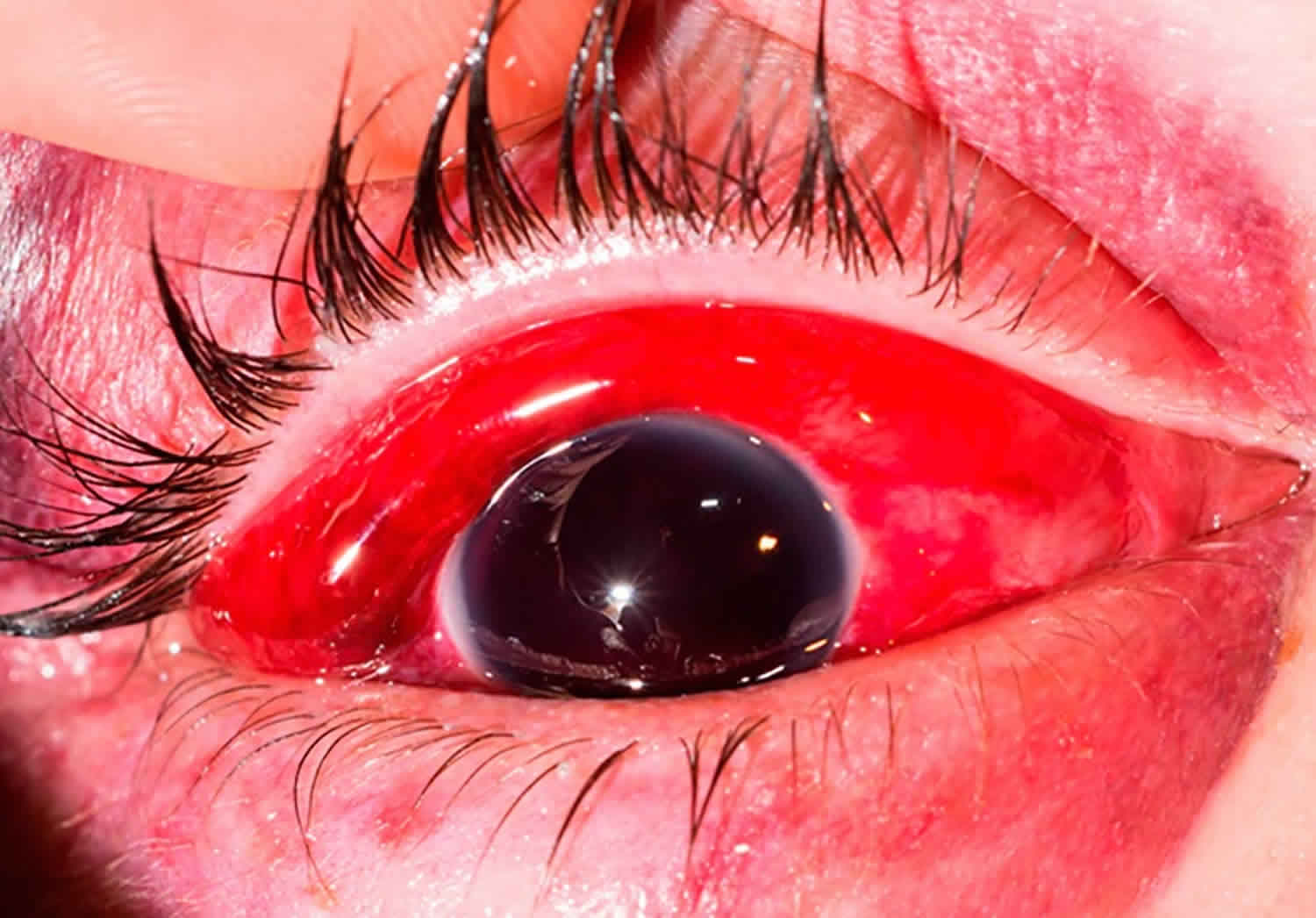
People dying natural deaths often have minor blunt force injuries that do not contribute to death - small abrasions or contusions on the skin are commonplace at autopsy. Bite wounds and chop injuries may be considered variants of blunt force trauma, sharp force trauma, or a class of injuries untothemselves.īlunt force trauma is routinely involved in cases classified as accidents, as well as in cases of suicide and homicide. Other deaths resulting from blunt force trauma involve jumping or falling from heights, blast injuries, and being struck by a firm object, such as a fist, crowbar, bat, or ball. For instance, almost all transportation fatalities - including those involving motor vehicle collisions, pedestrians being struck by vehicles, airplane crashes, and boating incidents - result from blunt force trauma. Whereas other forms of traumatic death (eg, gunshot wounds, sharp force injuries) occur under a relatively limited number of circumstances, deaths resulting from blunt force trauma occur in a variety of scenarios. Deaths resulting from blunt force trauma are some of the most common cases encountered by the practicing forensic pathologist.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
